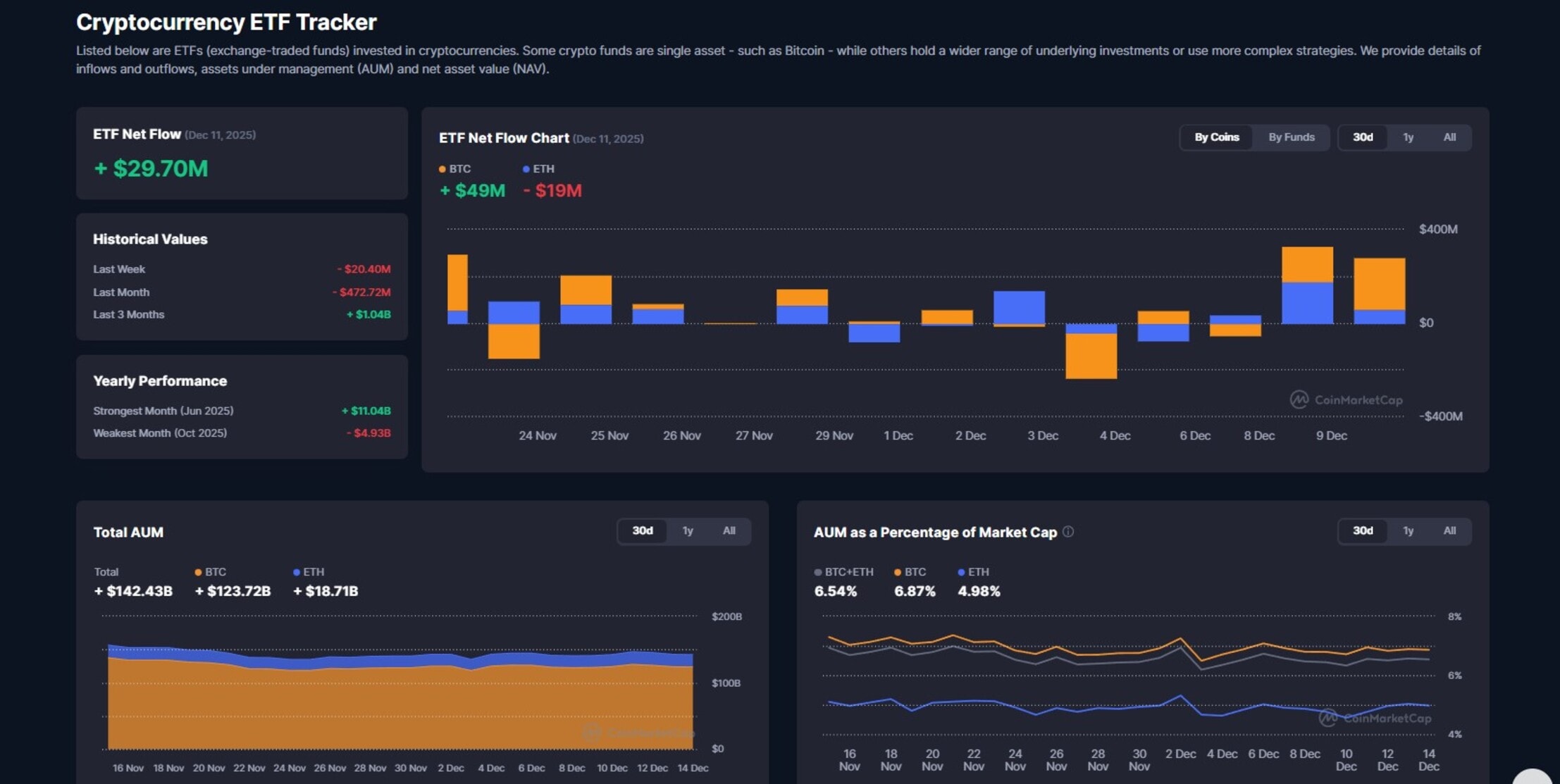
Crypto ETFs are exchange-traded funds that provide investors with exposure to cryptocurrencies without needing to buy, own, store, or manage the digital assets directly. These investment products are traded on traditional stock exchanges and work like traditional ETFs, but they track the prices of crypto assets, crypto indexes, or companies connected to the crypto industry.
If you’ve been wondering what ETFs in crypto ETFs are, this article dives into everything you need to know about crypto ETFs, including how they work, their types, and benefits. Additionally, we throw more light on their limitations, how to invest, regulations around crypto ETFs, and alternative investment options. Let’s dive in!
What Is a Crypto ETF?

Crypto ETFs are exchange-traded funds that provide investors with exposure to cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum without needing to own or manage the assets directly. They trade on traditional stock exchanges, mirroring the price movements of underlying digital currencies through shares bought and sold like stocks.
There are two types of cryptocurrency ETFs, which are spot ETFs and futures ETFs. Spot ETFs hold actual cryptocurrencies in custody, ensuring direct price tracking, while crypto futures ETFs use derivative contracts to bet on price directions without physical ownership.
Crypto ETFs offer traders convenience, regulatory oversight, liquidity, and tax efficiency. However, risks include market volatility, management fees, counterparty exposure in futures, and no direct crypto redemption for shares.
How Does a Cryptocurrency ETF Work?

A cryptocurrency ETF works by tracking the price of cryptocurrencies so investors can gain exposure without buying the coins directly. A Bitcoin ETF, for example, moves in value with Bitcoin’s price. Crypto ETFs are traded on stock exchanges just like regular stocks, making them easy to buy and sell.
This simplifies crypto investing but still carries risks from market swings and management fees. Investors can choose between ETFs that hold the actual cryptocurrency or those that use futures contracts and derivatives products to follow price movements.
This gives options for different risk levels and investment strategies. Crypto ETFs also make it easier to diversify by tracking multiple cryptocurrencies in a single fund. Overall, they provide a simpler, regulated way to invest in crypto assets compared to buying them directly.
Types of Cryptocurrency ETFs
The main types of cryptocurrency ETFs are highlighted below:
Spot Crypto ETFs
Spot crypto ETFs hold actual cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin or Ethereum in secure custody, ensuring the fund’s value directly reflects the coins’ market price. This structure allows investors to gain exposure to digital coins without managing wallets, private keys, or exchanges, simplifying participation in the crypto market.
By eliminating the technical challenges of direct ownership, investors can focus on tracking performance and making informed investment decisions. These cryptocurrency exchange-traded funds are particularly suitable for investors seeking precise tracking of coin prices within a regulated environment.
Spot ETFs also allow portfolio diversification by including multiple cryptocurrencies in a single fund, spreading risk across different digital currencies. While market volatility still affects returns, the transparency and straightforward nature of ownership make spot ETFs a practical option for both new and experienced investors.
Crypto Futures ETFs
Futures crypto ETFs do not hold the actual cryptocurrency but instead use derivative contracts that speculate on the coin’s future price. This means the ETF’s value changes based on market expectations rather than the real-time price of the underlying asset.
Investors gain exposure to price movements without needing to manage digital wallets or private keys, which can simplify trading for those focused on market trends. Futures ETFs are well-suited for investors interested in short-term strategies or hedging against market fluctuations.
However, because the contracts can deviate from actual crypto prices, volatility may be higher compared to spot ETFs. Understanding how these contracts work and monitoring market conditions closely is essential for anyone considering this type of investment.
Benefits of Investing in Crypto ETFs
The benefits of investing in cryptocurrency ETFs include accessibility, simplicity, portfolio diversification, liquidity, improved security, and tax efficiency.
1. Accessibility and Simplicity
Crypto ETFs make investing in digital assets easier for individuals who want exposure without managing wallets, private keys, or cryptocurrency exchanges. By trading on traditional stock exchanges, investors can buy and sell shares just like any other stock.
This removes technical barriers and enables both new and experienced investors to enter the markets without dealing with the complexities of direct coin ownership. Accessibility also supports better portfolio management because investors can monitor and adjust positions easily through a brokerage account.
The simplicity of this approach allows a focus on strategy and market trends rather than on security and custody, which are handled by funds or investment companies.
2. Diversification
Crypto ETFs often include exposure to more than one cryptocurrency within a single fund, which reduces reliance on the performance of one asset. Making diversification becomes easier without the need to buy and manage several cryptocurrencies separately, since exposure to multiple assets is already built into a single investment.
This structure allows portfolios to spread risk more effectively across the crypto market rather than depending on the performance of one coin. As a result, long-term portfolio balance improves, reducing the pressure to react to sharp price swings in individual assets while maintaining a clear and organized investment structure.

3. Liquidity
Crypto ETFs trade on traditional stock exchanges throughout the market day, allowing investors to buy or sell positions at current market prices. This continuous trading access makes it easier to respond to price movements without long delays, even during periods of higher market activity.
Compared to direct crypto trading, pricing remains more consistent and easier to follow. Reliable liquidity also supports better control over portfolio adjustments as cryptocurrency market conditions change. Positions can be increased, reduced, or exited without disrupting overall investment plans.
4. Enhanced Security
Crypto ETFs reduce personal security risks by placing custody of digital assets with professional fund managers. This structure removes the need to store private keys, manage wallets, or secure access credentials. Exposure to cryptocurrency remains intact while responsibility for asset protection shifts to institutions built for that purpose.
Institutional custody often includes regulated storage systems, internal controls, and insurance coverage. These safeguards lower the chances of loss caused by technical errors or unauthorized access. As a result, investors can participate in crypto markets with greater confidence while avoiding the security challenges of direct ownership.
5. Tax Efficiency
Crypto ETFs reduce personal security risks by placing custody of digital assets with professional fund managers. This structure removes the need to store private keys, manage wallets, or secure access credentials. Exposure to cryptocurrency remains intact while responsibility for asset protection shifts to institutions built for that purpose.
Institutional custody often includes regulated storage systems, internal controls, and insurance coverage. These safeguards lower the chances of loss caused by technical errors or unauthorized access. As a result, investors can participate in crypto markets with greater confidence while avoiding the security challenges of direct ownership.
Drawbacks of Investing in Crypto ETFs
The limitations of investing in cryptocurrency ETFs include market volatility, lack of direct ownership, management fees, and tracking errors.
1. Market Volatility
Crypto ETFs remain closely tied to the price movements of cryptocurrencies, which are known for sharp and unpredictable swings. When the cryptocurrency market experiences rapid price changes, ETF values move in the same direction, sometimes within short periods. This exposure means losses can occur quickly during downturns, even within a regulated investment structure.
Volatility also affects decision-making, especially during market stress. Sudden price drops can trigger emotional reactions or rushed portfolio adjustments. Understanding this risk is important, as crypto ETFs do not eliminate market instability but package it into a more accessible format.
2. Lack of Direct Ownership
Investing in a cryptocurrency ETF does not provide ownership of the actual cryptocurrency. Instead of holding coins, investors own shares of a fund that tracks crypto prices. This separation means there is no control over private keys or access to on-chain features associated with digital assets.
Without direct ownership, participation in activities such as staking, transferring coins, or using decentralized applications is not possible. Exposure remains limited to price movements alone, which may not suit investors seeking full involvement in the crypto ecosystem.
3. Management Fees
Crypto ETFs charge management fees to cover fund operations, custody, and administration. These fees reduce overall returns over time, especially for long-term investors. Even small annual fees can have a noticeable impact when compounded across several years.
Fee structures also vary between crypto exchange-traded funds, making cost comparison an important step before investing. Higher ETF fees may be justified by better custody or liquidity, but careful evaluation helps ensure costs do not outweigh potential gains.
4. Tracking Errors
Some crypto ETFs, especially futures based funds, may not perfectly match the price of the underlying cryptocurrency. Differences can occur due to contract rollovers, market conditions, or fund structure. This creates gaps between ETF performance and actual crypto price movement.
Tracking errors can become more noticeable during volatile markets or over extended holding periods. Understanding how closely an ETF follows its intended benchmark helps set realistic expectations and prevents surprises in performance outcomes.
How to Invest in Crypto ETFs
Crypto ETFs offer two primary investment approaches: trading via CFDs for leveraged speculation without ownership, or buying direct shares for actual exposure through regulated funds. CFDs are ideal for short-term traders, while direct purchases appeal to long-term holders seeking simplicity and custody.
Trading crypto exchange-traded funds using CFDs
CFDs allow speculating on ETF price movements without owning shares or underlying crypto, profiting from rises (long) or falls (short) via contracts with brokers. Leverage up to 1:10 amplifies positions but heightens risks like margin calls and overnight swaps; platforms like eToro, Exness, and AvaTrade offer crypto ETF CFDs with 24/5 trading.
Steps for investing via CFDs
- Sign up with a CFD broker like AvaTrade, eToro, or FXTM that supports crypto ETFs.
- Complete KYC and fund your account via bank transfer or card.
- Search for the specific ETF CFDs you want to trade (e.g., Bitcoin ETF CFD)
- Then, select position size with leverage (up to 1:10), and place long/short orders with stop-loss. You can monitor your trades, close positions manually or via trailing stops to lock in profits during high-volatility periods.
Buying cryptocurrency ETFs directly
Direct purchases involve buying ETF shares on stock exchanges like the NYSE, thereby granting indirect crypto exposure through funds that hold actual assets (spot ETFs) or futures.
This method uses standard brokerage accounts, incurs expense ratios (0.20-0.53%), and enables tax-advantaged holding in IRAs or TFSAs. Ownership remains with the ETF issuer, simplifying access over direct crypto buys while tracking prices closely during market hours.
Steps for direct ETF purchases
- Open a brokerage account with platforms like Fidelity, BlackRock, or TD Ameritrade that offer crypto ETFs.
- Verify your identity and deposit funds.
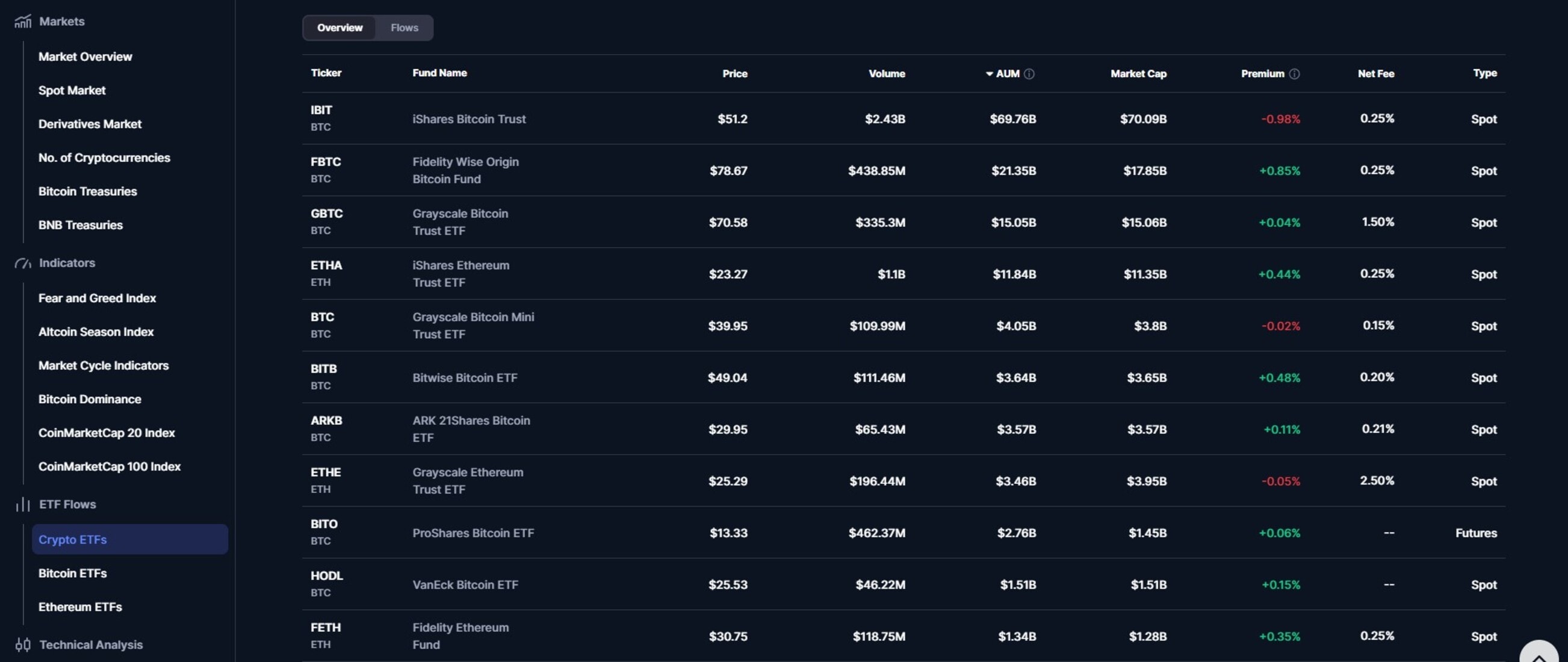
- Research tickers (IBIT for BlackRock BTC ETF, ETHA for Ethereum), review fees and AUM, then buy shares via market/limit orders during exchange hours.
- Hold in retirement accounts if you’re eligible; rebalance periodically and track net asset value (NAV).
Regulations on Crypto ETFs
Crypto ETF regulations have advanced over the years, particularly in the US. Currently, streamlined Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) approvals enable faster launches of spot ETFs for assets like Bitcoin, Ether, and Solana. Here’s a more detailed breakdown of the global regulatory environment on crypto ETFs.
US SEC framework
The SEC approved generic listing standards for spot commodity-based ETFs, including crypto, in September 2025. This move allows traditional stock exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), Nasdaq, and Cboe to list products without individual reviews if the criteria are met.
Key requirements include the underlying asset having futures traded on a regulated exchange like Coinbase for at least six months, or an existing ETF holding at least 40% direct exposure to it. Additional changes permit in-kind creations/redemptions, options on Bitcoin ETPs, and mixed Bitcoin-Ether products, boosting efficiency and inflows.
Global crypto ETFs regulations overview
In the EU, cryptocurrency ETFs face stricter rules under MiFID II and UCITS, which restrict single-asset, highly volatile holdings like Bitcoin for retail investors, though workarounds exist via professional investor products. BaFin in Germany has explicitly barred Bitcoin-only UCITS ETFs. Broader 2025 global trends show increased coordination, such as the US CFTC-SEC alignment on spot products, but oversight varies widely across jurisdictions.
Alternatives to Crypto ETFs
1. Crypto Trusts
Crypto trusts, often called closed-end trusts or Grayscale-style products like GBTC, provide indirect crypto exposure by holding actual cryptocurrencies in custody while issuing a fixed number of shares that trade on stock exchanges. Unlike open-end ETFs, they do not create or redeem shares based on demand, leading to potential premiums or discounts to net asset value (NAV).
The key difference between Grayscale investments and crypto ETFs is that crypto trusts maintain a fixed share supply, allowing managers to pursue long-term strategies without redemption pressure. However, shares often trade at discounts (e.g., GBTC has historically traded at 20-40% below NAV) due to lower liquidity.
2. Crypto ETPs
Crypto ETPs, or Exchange-Traded Products, are securities traded on stock exchanges that track the price of cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin or Ethereum, providing exposure without direct ownership. They encompass ETFs, ETCs (exchange-traded commodities), and ETNs (exchange-traded notes), using physical backing (holding actual crypto) or synthetic methods (swaps with collateral).
3. Companies That Hold Crypto
Companies that hold crypto include custodians that secure assets for institutions, ETFs, and exchanges, as well as public firms with significant balance-sheet allocations. Custodians like Coinbase Custody manage over $193 billion in assets using cold storage and insurance, while others, such as BitGo and Anchorage Digital, provide regulated, multi-signature solutions.
4. Crypto-Related ETFs
Crypto-related ETFs go beyond direct Bitcoin or Ethereum spot products to include futures-based, mixed-asset, leveraged, and thematic funds that track crypto proxies such as miners or blockchain firms. These provide diversified or amplified exposure while trading on major exchanges.
Conclusion
A crypto ETF is simply a regulated investment fund that tracks the price of a cryptocurrency and trades on a traditional stock exchange. It offers a more straightforward way to gain crypto exposure without dealing directly with wallets, private keys, or crypto exchanges.
As for the best crypto ETF to invest in, the right choice depends on factors such as the type of exposure you want (spot or futures-based), the ETF’s fees, liquidity, tracking accuracy, and the regulatory environment in which it operates. Your risk tolerance, investment timeline, and portfolio goals should also guide the decision.
FAQs
Yes, crypto ETFs can be traded on traditional stock exchanges. You buy and sell them through a regular brokerage account without needing a crypto wallet. The ETF’s price changes as the value of the underlying cryptocurrency moves. This allows both professional and retail investors to access crypto markets easily and safely.
A crypto ETF can be a good investment for investors who want exposure to cryptocurrency without buying or storing digital coins directly. It offers a regulated and familiar way to participate in crypto price movements through a brokerage account.
However, returns still depend on market volatility, fees, and whether the exchange-traded fund holds actual cryptocurrency or uses futures contracts. It suits investors seeking convenience and lower technical risk rather than full control of crypto assets.
BlackRock’s iShares Bitcoin Trust (IBIT) ranks as the top crypto ETF among most investors due to its massive $70B+ AUM, a low 0.25% fee, and deep liquidity from strong inflows. Fidelity’s FBTC offers similar reliability at 0.25% with strong performance (+64% YTD).
Meanwhile, ARK 21Shares Bitcoin ETF (ARKB) stands out for its 0.21% fee. The best crypto ETF for you depends on your goals. However, as a rule of thumb, prioritize spot BTC for core holdings and avoid leveraged products like BITX unless you are trading short-term.
Bitcoin ETFs are exchange-traded funds that track Bitcoin’s price by holding the cryptocurrency directly (spot ETFs) or via futures contracts, allowing investors to gain exposure through traditional brokerage accounts without managing wallets. Bitcoin ETFs were approved by the SEC in January 2024, and they currently trade on major exchanges like the NYSE.
An Ethereum ETF tracks the price of Ethereum (ETH), the second-largest cryptocurrency by market cap. It allows investors to gain exposure to ETH’s price movements by buying shares on traditional stock exchanges like the NYSE, without storing or managing the cryptocurrency themselves.
Yes, spot crypto ETFs are approved in the U.S. by the SEC for major cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum. Spot Bitcoin ETFs launched in January 2024 following SEC approval of 11 funds. Meanwhile, spot Ethereum ETFs got approved in May 2024.
As of late 2025, the SEC has streamlined approvals with new generic listing standards. This development reduced review times to 75 days as opposed to 240 days for qualifying crypto ETFs tied to assets like Solana or XRP.
No, XRP is not an ETF. XRP cryptocurrency is built to facilitate fast cross-border transactions. If you’re asking whether the XRP ETF is approved for trading, the answer is YES. XRP ETFs have been approved and are now trading in the US. Major firms like Bitwise, Grayscale, and 21Shares launched spot XRP funds in late 2025 following approval from the SEC.
